Blazars and other galaxies with active nuclei have been a significant focus of RCT research, as queue scheduled observations have facilitated monitoring the variable energy output of these sources. These data are then combined with observations by collaborators at other wavelengths, providing a clearer picture of the behavior of the material in the relativistic jet and central engine.
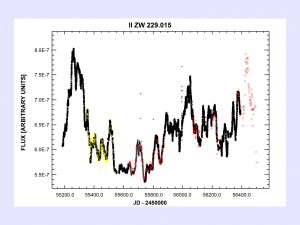

Composite light curve for the well-known AGN II ZW 229.015, showing data from the RCT (red), Barth et al. (2011, yellow), and the Kepler satellite. RCT image of II ZW 229.015 to the right taken on 06/05/2013.
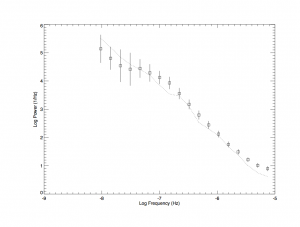
The complete data set analyzed by Williams and Carini (2013) yields a break in the slope of the Power Spectrum Density (PSD) which implies a central black hole mass of 12 million solar masses, as shown in the above graph.
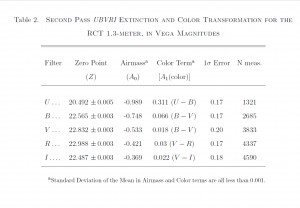
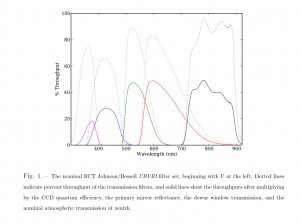 and zero points. Click for a sharper view of the figure or table.
and zero points. Click for a sharper view of the figure or table.